Use of patch files
Between releases of authorised SWAN versions, it is possible that bug fixes or new
features are published on the SWAN homepage. These are provided by patch files that can
be downloaded from the website. Typically, a patch can be installed on top of the
existing source code. Patches are indicated by a link to patchfile. The names
refer to the current version number supplemented with letter codes. The first will be
coded 'A' (i.e. 41.51.A), the second will be coded 'B', the third will be coded 'C', etc.
The version number in the resulting output files will be updated to 41.51ABC, indicating
the implemented patches.
To use a patch file, follow the next instructions:
- download the file (right-click the file and choose save link as)
- place it in the directory where the source code of SWAN is located
- execute patch -p0 < patchfile
After applying a patch or patches, you need to recompile the SWAN source code.
It is important to download the patch and not cut and paste it from the display
of your web browser. The reason for this is that some patches may contain tabs,
and most browsers will not preserve the tabs when they display the file. Copying
and pasting that text will cause the patch to fail because the tabs would not be
found. If you have trouble with patch, you can look at the patch file itself.
Note to Linux/UNIX users:
the downloaded patch files are MS-DOS ASCII files and contain carriage return (CR) characters.
To convert these files to UNIX format, use the command dos2unix. Alternatively,
execute cat 41.51.[A-C] | tr -d '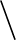 r' | patch that apply the patch files
41.51.A to 41.51.C to the SWAN source code at once after which the conversion is
carried out.
r' | patch that apply the patch files
41.51.A to 41.51.C to the SWAN source code at once after which the conversion is
carried out.
Note to Windows users: patch is a UNIX command. Download the patch program
from the SWAN website, which is appropriate for Windows operating system.
The SWAN team 2024-09-09
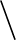 r' | patch that apply the patch files
41.51.A to 41.51.C to the SWAN source code at once after which the conversion is
carried out.
r' | patch that apply the patch files
41.51.A to 41.51.C to the SWAN source code at once after which the conversion is
carried out.